Adsorption
Introduction
There are several examples, which reveal that the surface of a solid has the
tendency to attract and retain the molecules of the phase with which it
comes into contact. Thesemolecules remain only at the surface and do
not go deeper into the bulk.
Adsorption
The accumulation of molecular species
at the surface rather than in the bulk of a solid or liquid is termed
adsorption.
Adsorbate
The molecular species or substance, which concentrates or
accumulates at the surface is termed adsorbate .
Adsorbent
The material on the
surface
of which the adsorption takes place is called adsorbent.
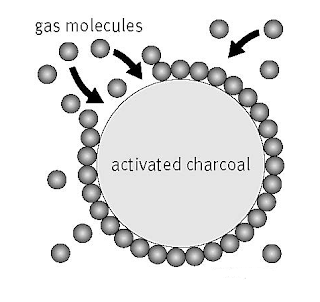
Adsorption in action
(i) If a gas like O2
, H2 , CO, Cl2 , NH3 or SO2 is taken in a closed vessel containing powdered charcoal, it is observed that the pressure of the gas in the enclosed vessel decreases. The gas molecules concentrate at the surface of the charcoal, i.e., gases are adsorbed at the surface.
(ii) In a solution of an organic dye, say methylene blue, when animal
charcoal is added and the solution is well shaken, it is observed
that the filtrate turns colourless. The molecules of the dye, thus,
accumulate on the surface of charcoal, i.e., are adsorbed.
(iii) Aqueous solution of raw sugar, when passed over beds of animal
charcoal, becomes colourless as the colouring substances are
adsorbed by the charcoal.
(iv) The air becomes dry in the presence of silica gel because the water
molecules get adsorbed on the surface of the gel.
Desorption
The process of
removing an adsorbed substance from a surface on which it is adsorbed is called desorption.
Types of
Adsorption
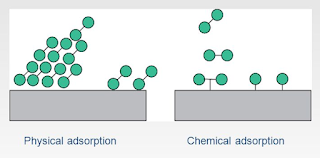
Physical
adsorption or physisorption:
If accumulation of gas on the surface of a solid occurs on account of
weak van der Waals’ forces, the adsorption is termed as physical
adsorption or physisorption.
Chemical adsorption or chemisorption:
When the gas molecules or atoms are
held to the solid surface by chemical bonds, the adsorption is termed chemical adsorption or chemisorption.
Highlight and copy the HTML below, then paste it into the code for your Web site
Highlight and copy the HTML below, then paste it into the code for your Web site

Chemisorption involves a high energy of
activation and is, therefore, often referred to as activated adsorption.
A physical adsorption at low
temperature may pass into chemisorption as the temperature is
increased.
For example:dihydrogen is first adsorbed on nickel by van
der Waals’ forces. Molecules of hydrogen then dissociate to form hydrogen
atoms which are held on the surface by chemisorption.


Comments
Post a Comment
Thanks for your comments